|
|
|
Residual stress measured in a metal matrix composite
M.B. Prime and M.R. Hill, 2004, "Measurement of Fiber-Scale
Residual Stress Variation in a Metal-Matrix Composite," Journal
of Composite Materials, 38(23), pp. 2079-2095. preprint (pdf)
. (LA-UR-03-4452)
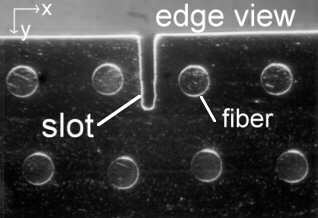
MMC Specimen:
- Kanthal matrix (weight % 73.2 Fe, 21 Cr, 5.8 Al, 0.04 C)
- 200 µm diameter Tungsten fibers
- 10 vol-% fiber content
- 15 mm X 23 mm X 2.5 mm
- Fibers run in 15 mm direction (see picture)
|
 |
Cut slot using wire EDM:
- Cut slot using 30 µm diameter Tungsten wire
- Resulting slot is 80 µm wide
- Slot cut in 25 µm increments to final depth of 0.5 mm
- Strain at each depth was measured with strain gage on top surface
|
 |
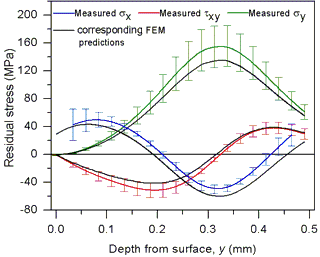
NEW Results:
- A more sophisticated analysis showed that there were shear stresses
in the measurement region
- Using inherent strain analysis, all 3 in-plane stress components
are determined
- Black curves are residual stress predictions from thermoplastic
finite element model. See paper (pdf)
for details.
|
 |
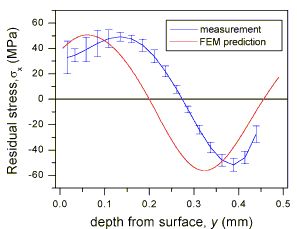
Old Results:
- Previously assumed shear stress τxy = 0
- Gave "shift" in answer
- Usually τxy is very small because it must be zero on the
surface and there is little to make it increase subsurface. However,
the poximity of fibers make it much larger in this case.
|
 |
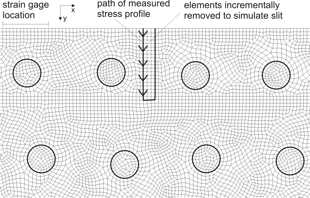
FEM
coefficients :
- Because of heterogeneous geometry, used FEM to calculate coefficients
- Mesh shown at right, zoomed in on portion from picture above
- See FAQ question about using FEM
|
|
NOTE: The raw data from this test and any other data from published
results can be made available for research purposes. Just email
me. |
|




