Los Alamos scientists win American Statistical Society award for computer model analysis method
This approach offers a new way to examine how two models behave together
Los Alamos researchers Scott Vander Wiel, Kellin Rumsey, Zachary Hardy and Cory Ahrens (now of Pacific Northwest National Laboratory) demonstrated a method to help make better use of computer models to simulate physical systems. Their work won the 2025 Statistics in Physical and Engineering Sciences Award.
Given by the American Statistical Association, the award recognizes individuals or teams for their innovative use of statistics to solve high-impact problems.
Why this matters: Sometimes scientists use multiple computer models at the same time, each based on different physical assumptions or with their own attributes. For example, in experimental design, several different materials may be under consideration and need evaluation. In this demonstration, the Los Alamos team guided scientific decisions about a set of simulated high-explosive experiments based on information about the alignment between models.
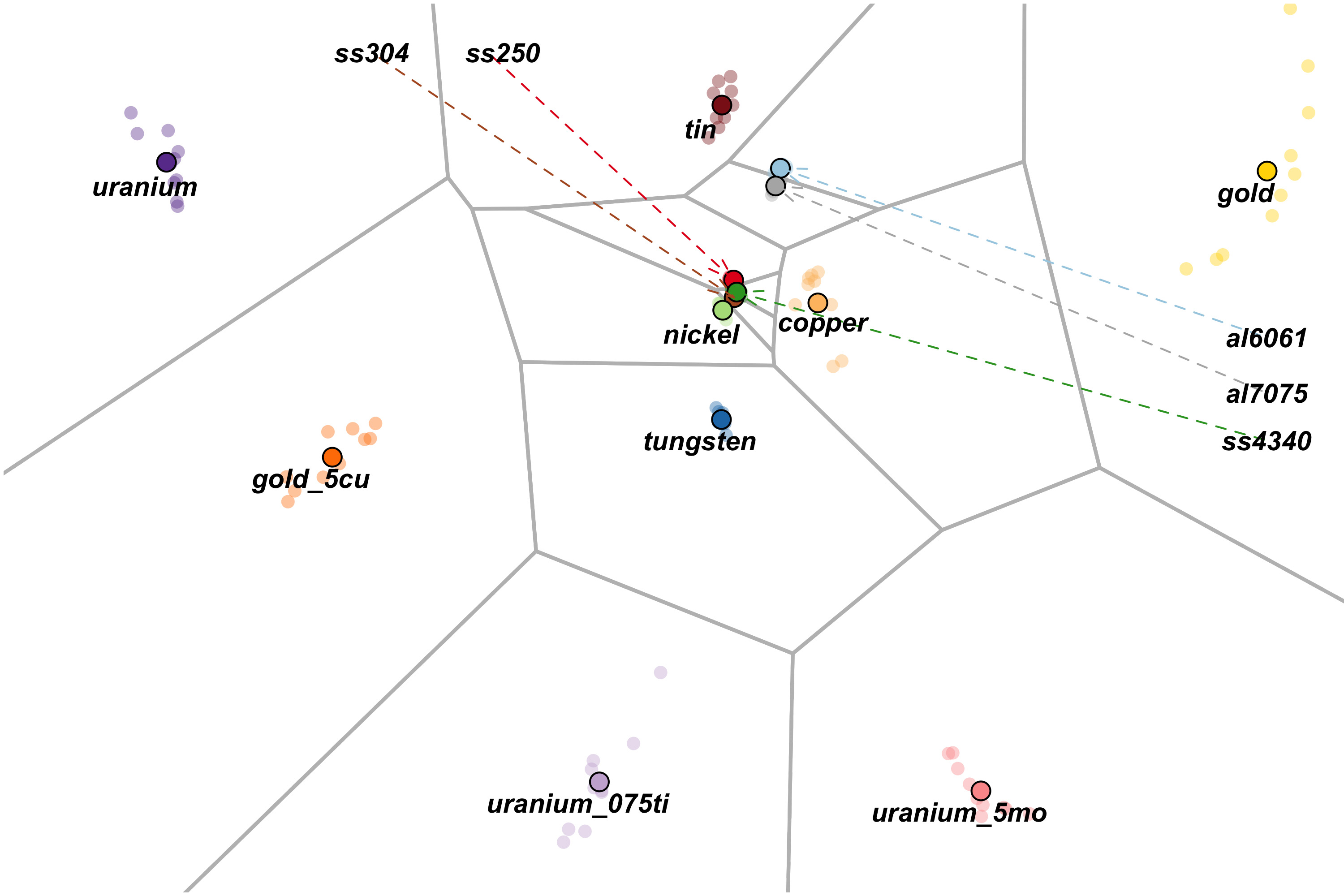
What they did: Lab statisticians used sophisticated machine learning techniques to estimate (or learn) the co-active subspaces of different computer models. The team developed a method that compares how computer models will react to changes in their inputs in relation to one another — specifically, whether the models respond to inputs in similar or different ways.
How it works: Using this co-active subspace method, scientists can:
· Identify which set of physical experiments will provide the most information about a physical system.
· Validate a new physical system by comparing it with trusted benchmarks, highlighting both alignment and areas that may need further investigation.
· Guide the design of more efficient simulations, saving time and reducing demands on high-performance computing resources.
Funding: The Engineering and Technology Maturation Program and Weapons Program Support – Design for Manufacturing at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
The paper: Co-Active Subspace Methods for the Joint Analysis of Adjacent Computer Models
LA-UR-25-28707