A Quantum Annealer Eigensolver (QAE) Developed, Implemented on D-Wave Machine
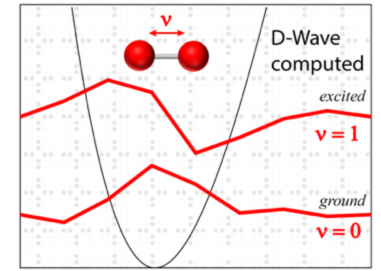
The quantum annealer eigensolver (QAE) is developed and applied to compute the vibrational spectrum of a molecule on LANL’s D-Wave machine “Ising”. The D-Wave computed ground and first excited state vibrational wave functions of O2 are plotted in red. The attractive interaction potential between the two oxygen atoms (red spheres) is plotted in black. The vibrational state is labeled by the quantum number ν where ν=0 is the ground state and ν=1 is the first excited state.
A new methodology to calculate the vibrational spectrum of a molecule on a quantum annealer
A Quantum Annealer Eigensolver (QAE) algorithm is developed to calculate the vibrational spectrum of a molecule on a quantum annealer. The method is demonstrated on LANL’s D-Wave machine “Ising” to compute the lowest two vibrational states of O2 (oxygen) and O3 (ozone). The algorithm is general and represents a new revolutionary approach to solving the real symmetric eigenvalue problem on a quantum annealer.